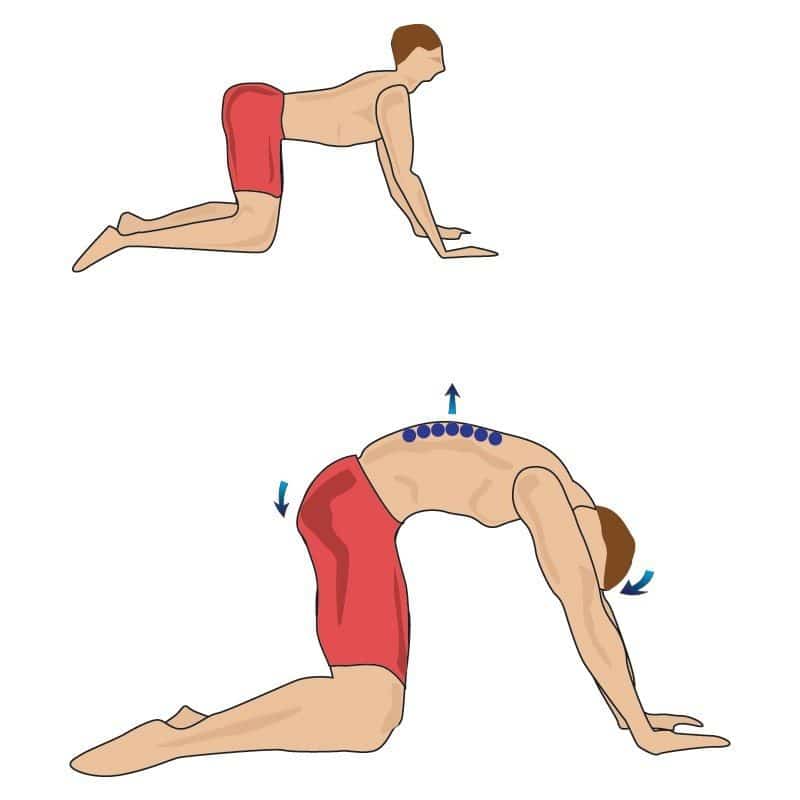
Cat Arch Back Stretch
What muscles does the cat arch back stretch target?
Erector Spinae
Spine
How to perform stretch:
Get down on all fours as per image
Release stomach and allow it to sag
Arch your back upwards
Anatomy:
The external most layers of abdominal muscle fibers are grouped as Rectus Abdominus muscle. These fibers stretch longitudinally from the ribs to the pubis. Their main action is trunk flexion.
There are three main erector spinae muscles – Iliocostalis Lumborum, Iliocostalis Thoracis and Longissimus. These muscles run in a longitudinal direction and are the major extensors of the trunk.
Serratus Posterior also leads to trunk extension when it acts bilaterally; however, its unilateral contraction leads to sideways flexion of the trunk as it pulls the outer angles of the ribs towards the spine.
The left and right Trapezius together form a trapezoid and each has three divisions: upper, middle and lower. The upper fibers contract to pull the scapula inwards and upwards. The upper trapezius is also responsible for head and neck extension, rotation and sideways flexion.
The middle and lower sections help to stabilize the thoracic spine along with the other spine extensor muscles. These fibers also pull the scapula inwards and downward.
Advantages:
This stretch affects the lumbar and thoracic spine both in flexion and in extension, as well as the abdominal, the lumbar and the thoracic erector spinae muscles.
It is an excellent stretch to work on your pelvis and it helps you to know how it moves during standing, walking, bending, running and leaping.
This stretch is a great help for posture, because pelvis is the main joint involved in all the postures – standing, moving or sitting. It forms the base of the trunk and its movement can greatly alter the shape and position of our trunk and the load distribution to the different muscles.
Regular Movements:
The spine should bend in both directions along its whole length. The range of movement may vary. The pelvis should be effectively pulled to make the coccyx (the tailbone) point outwards.





